Appearance
前端大屏适配几种方案
一、方案一:rem+font-size
动态设置HTML根字体大小和body字体大小,会使用到lib-flexible.js插件
lib-flexible.js
xml
(function flexible(window, document) {
var docEl = document.documentElement
var dpr = window.devicePixelRatio || 1
// adjust body font size
function setBodyFontSize() {
if (document.body) {
document.body.style.fontSize = (16 * dpr) + 'px'
}
else {
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', setBodyFontSize)
}
}
setBodyFontSize();
function setRemUnit() {
var rem = docEl.clientWidth / 24
docEl.style.fontSize = rem + 'px'
}
setRemUnit()
// reset rem unit on page resize
window.addEventListener('resize', setRemUnit)
window.addEventListener('pageshow', function (e) {
if (e.persisted) {
setRemUnit()
}
})
// detect 0.5px supports
if (dpr >= 2) {
var fakeBody = document.createElement('body')
var testElement = document.createElement('div')
testElement.style.border = '.5px solid transparent'
fakeBody.appendChild(testElement)
docEl.appendChild(fakeBody)
if (testElement.offsetHeight === 1) {
docEl.classList.add('hairlines')
}
docEl.removeChild(fakeBody)
}
}(window, document))我们可以将它下载下来。打开js文件,将设计稿的宽度(1920px)平均分成24等份,每一份为80px。将这个值设置为html字体大小,既1rem = 80px; 24rem = 1920px。
tips:rem是根据html字体大小来计算的,假如html字体为16px,则1rem就等于16px;
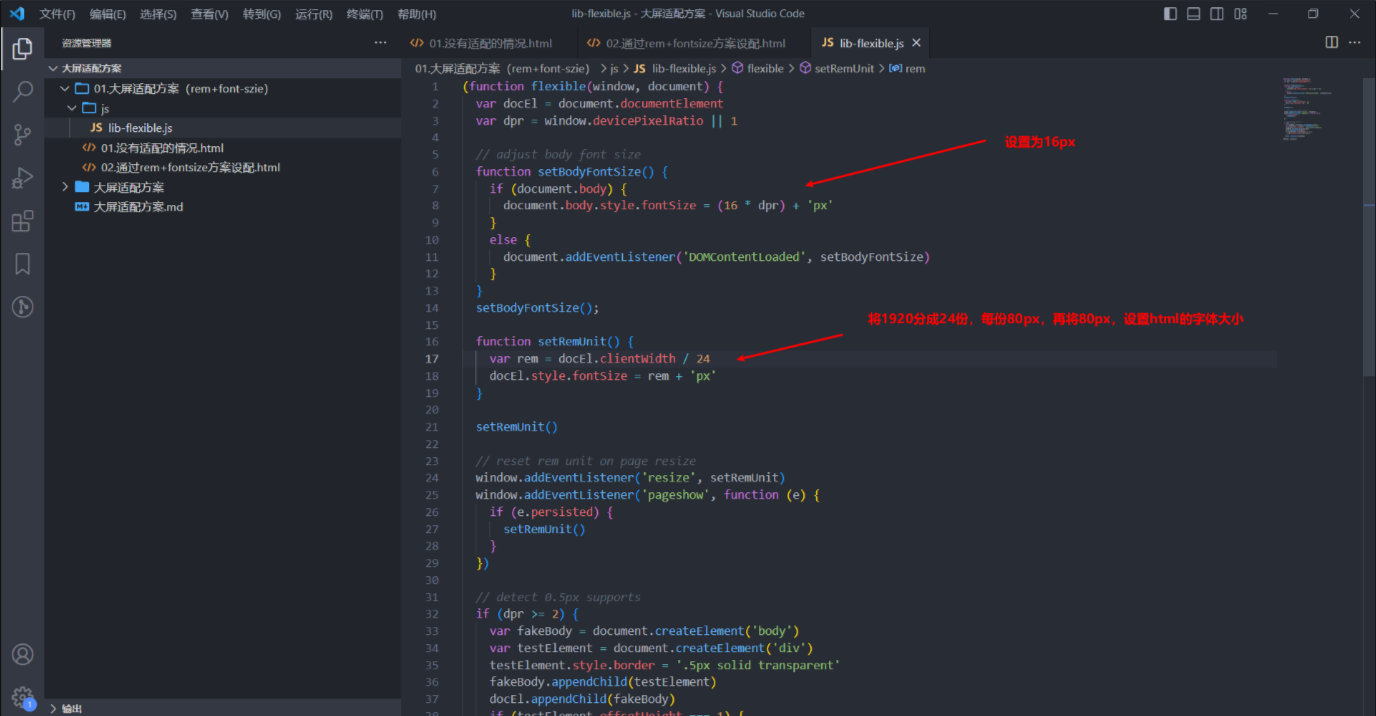
在移动端通常会分成10份,PC端分成24份。
安装cssrem插件,根节点的字体大小设置为80px。这个是px单位转rem的参考值。
配置插件的基准值:
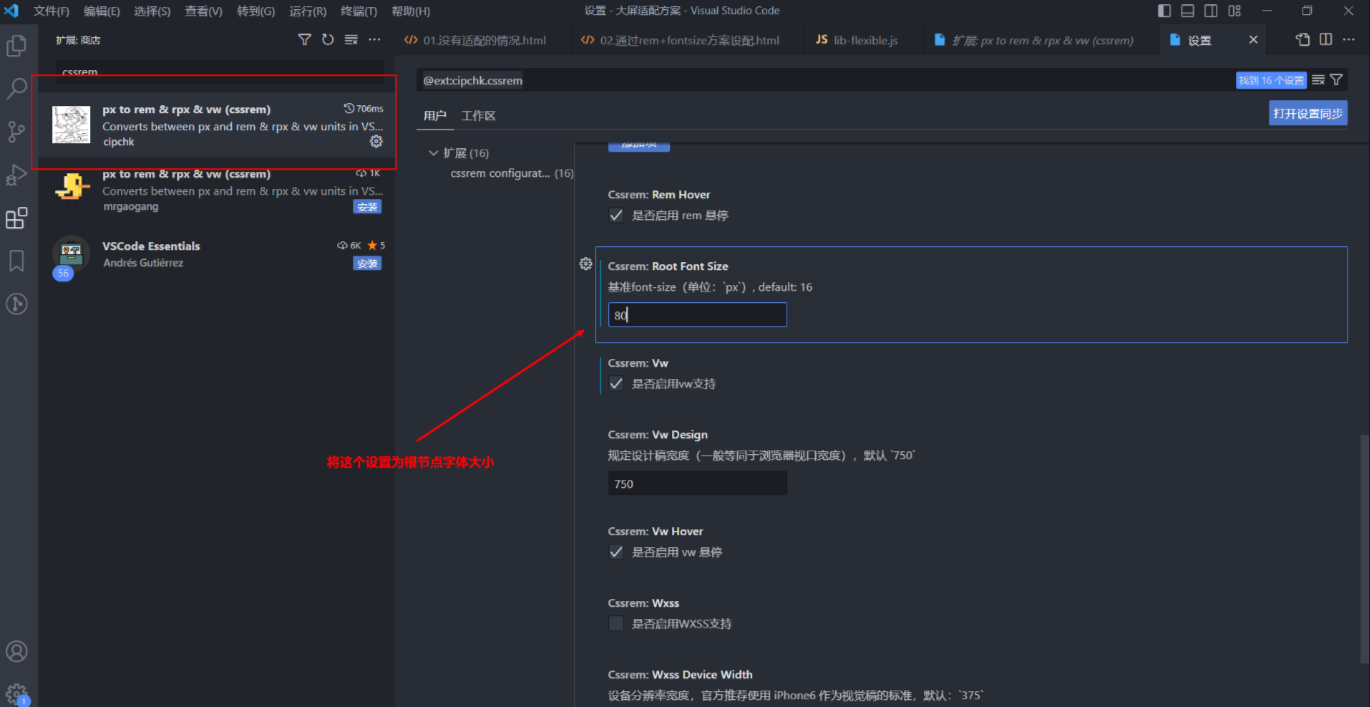
这样的话放我们在书写px的适合,这个插件就会自动帮我们转化成rem。
xml
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
width: 24rem;
height: 13.5rem;
border: 3px solid red;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
ul {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
li {
width: 33.333%;
height: 50%;
font-size: 0.375rem;
list-style: none;
border: 3px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
</ul>
</body>
<script src="./js/lib-flexible.js"></script>
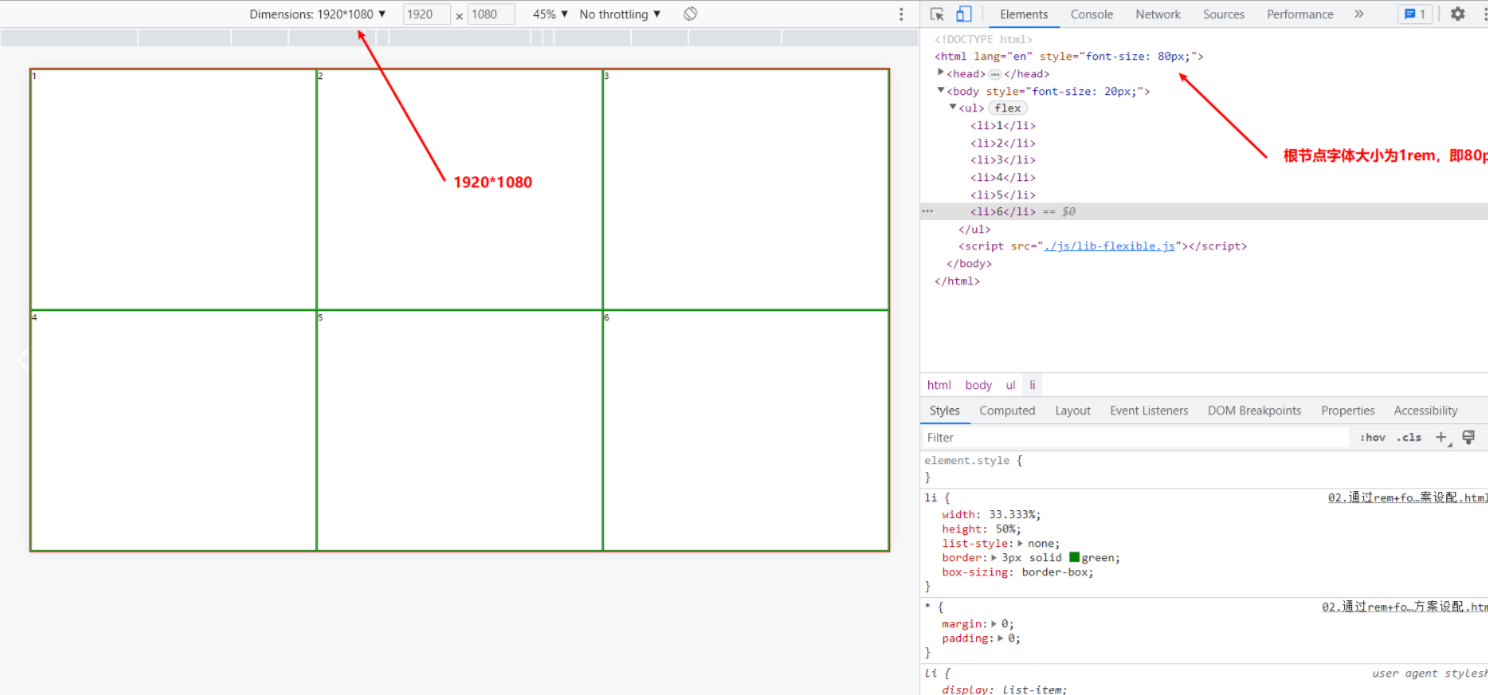
</html>1.查看适配情况
1.1 1920*1080情况下
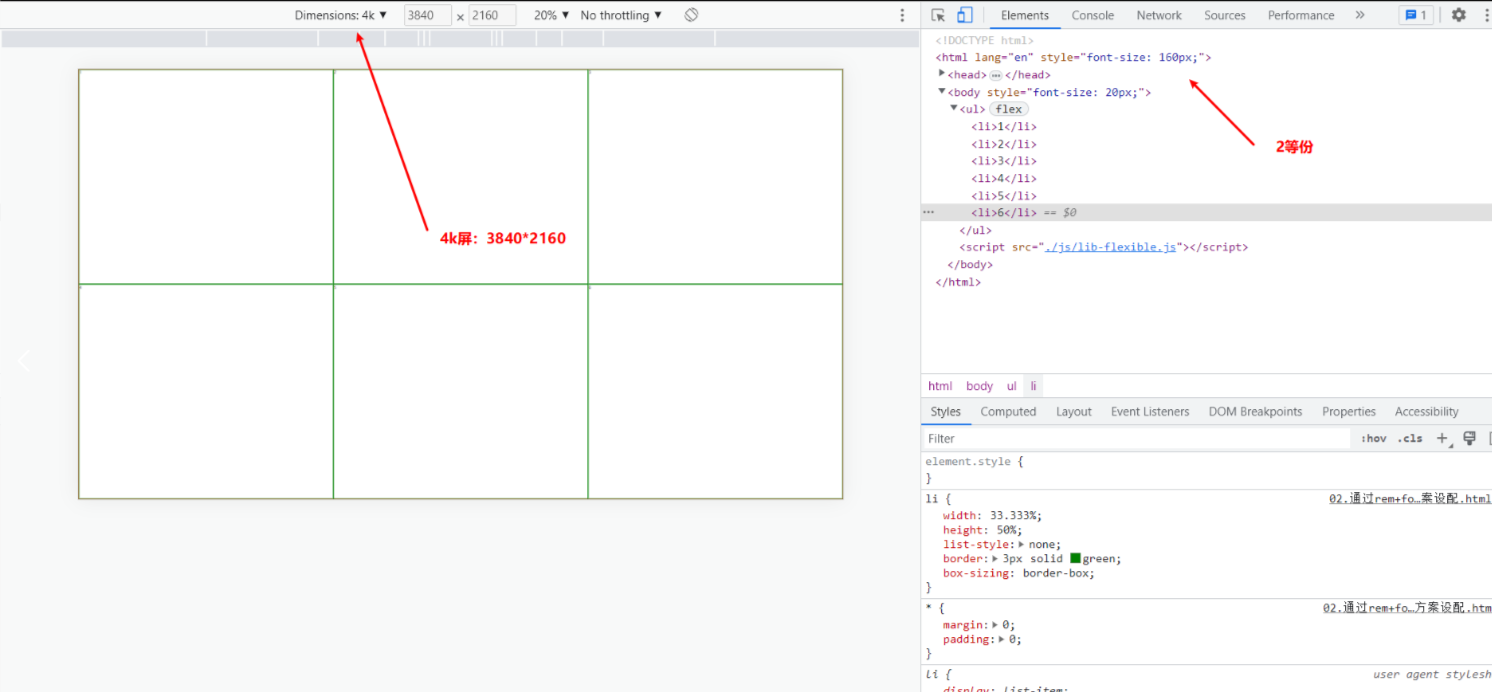
1.2 3840*2160(4k屏)情况下
3840也是分成24等份:3840 / 24 = 160
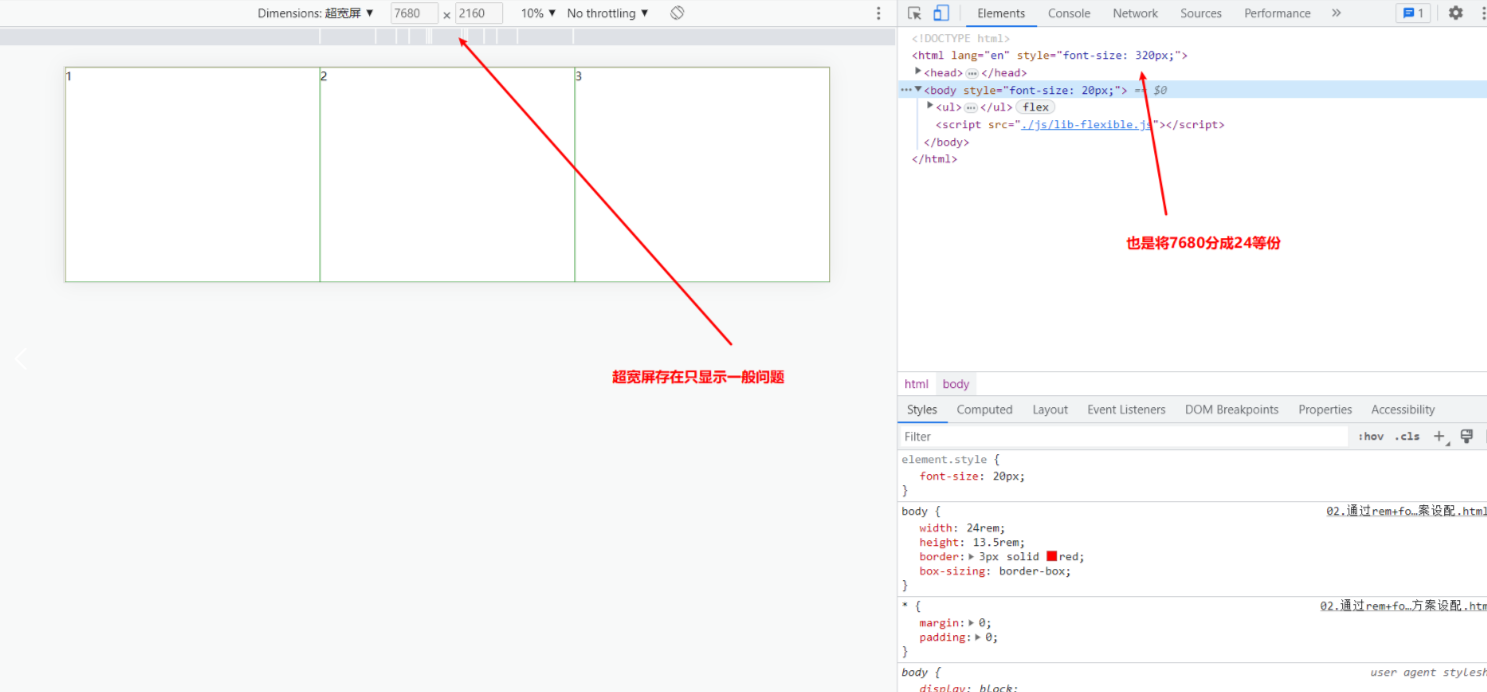
1.3 7680*2160 超宽屏下
超宽屏情况下只显示了上半部分,这种适配方式比较适合16:9的情况下使用,后面会有其他方案解决这个问题。
二、方案二:vw(单位)
直接使用vw单位,屏幕宽度默认为100vw,那么100vw = 1920px;1vw = 19.2px。这个也是使用cssrem插件,直接将body的宽高(1920px * 1080px),将px转成vw单位。
这种方案和第一个方案类似,超宽屏的情况下也是不能全部显示
xml
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
width: 100vw;
height: 56.25vw;
border: 3px solid red;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
ul {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
li {
width: 33.333%;
height: 50%;
font-size: 1.5625vw;
list-style: none;
border: 3px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>三、方案三:scale(缩放)
很多的大屏适配都是使用的这种方案。这种方案的原理就是根据宽高比例进行缩放。
1. 根据宽度比率进行缩放
(宽度比率=网页当前宽度/设计稿宽度)
xml
<script>
// 设计稿:1920 * 1080
// 1.设计稿尺寸
let targetWidth = 1920;
// 2.拿到当前设备(浏览器)的宽度
// document.documentElement 获取html的宽度
let currentWidth =
document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth;
// 3.计算缩放比率(屏幕过宽,根据高度计算缩放比例)
let scaleRatio = currentWidth / targetWidth;
// 4.开始缩放网页
document.body.style = `transform: scale(${scaleRatio})`;
</script>上面这种根据宽度比例进行缩放的,针对1920 * 1080,3840 * 2160(4k)是没有问题的,但是在超宽屏的情况下还是存在只显示一半的问题。
分析原因:
xml
我们的设计稿:
1920 * 1080 => 要适配 (1920*2=3840, 1080*2=2160, 4k屏) 3840 * 2160
也要适配=> ( 1920*4 = 7680 : 1080 * 2 = 2160) 7680 * 2160
我们当前是根据宽度比率进行缩放的:
先设配3840 * 2160
scaleRatio = 3840 / 1920 = 2
根据这个缩放比率
我们的设计稿宽高都会被缩放两倍
1920 * 2 = 3840
1080 * 2 = 2160
设配7680 * 2160
scaleRatio = 7680 / 1920 = 4
根据这个宽度比例我们的设置稿宽高都会被缩放4倍
1920 * 4 = 7680
1080 * 4 = 4240
这个原先的比例是 4 : 2,现在变成了 4 :4 ,这也是为什么我们只看到一半高度的原因。2. 动态计算
动态计算网页宽高比,决定是按照宽度的比例还是高度的比例进行缩放。
xml
<script>
// 设计稿:1920 * 1080
// 1.设计稿尺寸
let targetWidth = 1920;
let targetHeight = 1080;
let targetRatio = 16 / 9; // 宽高比率 (宽 / 高)
// 2.拿到当前设备(浏览器)的宽度和高度
let currentWidth =
document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth;
let currentHeight =
document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight;
// 3.计算缩放比率(屏幕过宽,根据高度计算缩放比例)
// 若currentWidth是4k屏宽度 3840 除于 我们设计稿的宽度 1920 3840/1920 = 2
// 这样页面就行进行2倍缩放
let scaleRatio = currentWidth / targetWidth; // 参照宽度进行缩放(默认情况下)
// 当前页面宽高比例,当页面越宽currentRatio值就越大
let currentRatio = currentWidth / currentHeight;
// 判断是根据宽度进行缩放,还是根据高度进行缩放
if (currentRatio > targetRatio) {
// 根据高度进行网页的缩放
scaleRatio = currentHeight / targetHeight; // 参照高度进行缩放(屏幕很宽的情况下)
document.body.style = `transform: scale(${scaleRatio}) translateX(-50%)`;
} else {
// 根据宽度进行网页的缩放
document.body.style = `transform: scale(${scaleRatio})`;
}
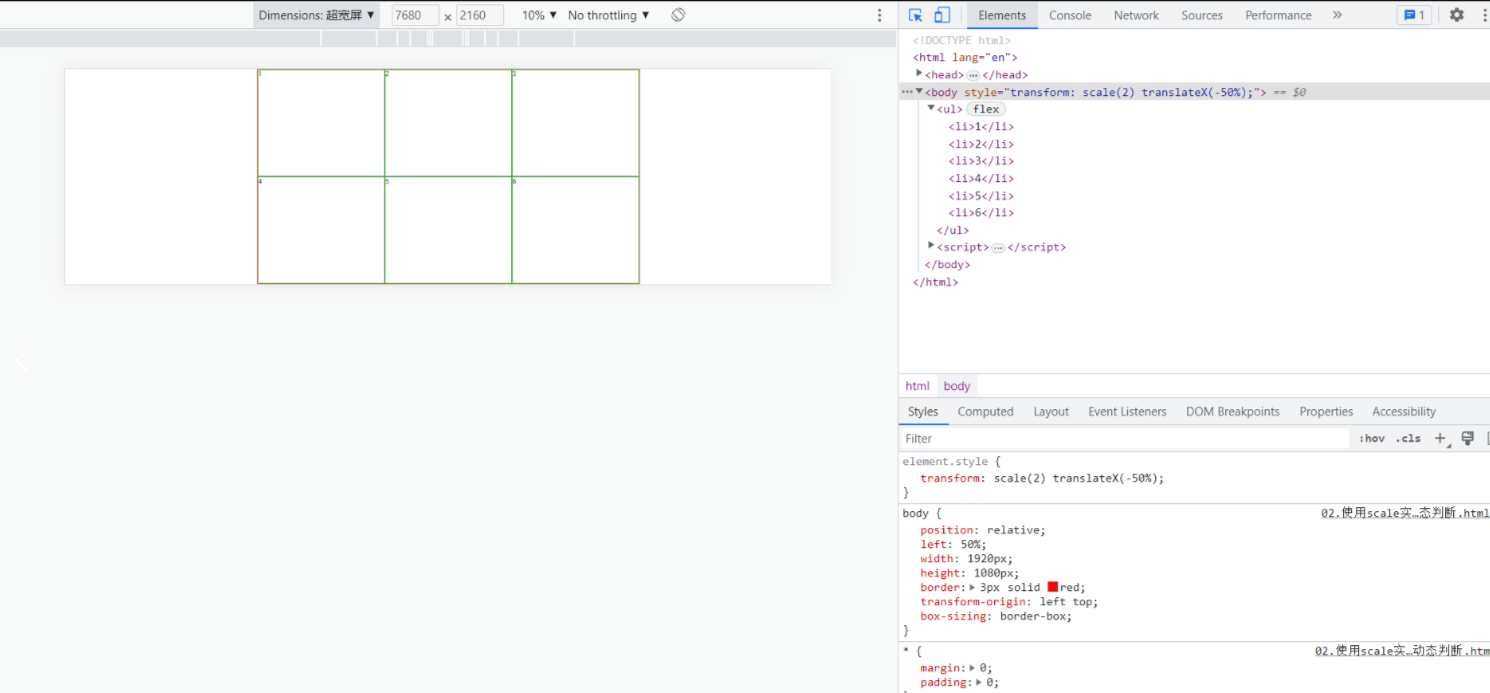
</script>2.1 超宽屏最终适配效果
完整demo代码:
xml
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
position: relative;
width: 1920px;
height: 1080px;
border: 3px solid red;
/* 设置缩放原点 */
transform-origin: left top;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
ul {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
li {
width: 33.333%;
height: 50%;
font-size: 30px;
list-style: none;
border: 3px solid green;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
</ul>
</body>
<script>
// 设计稿:1920 * 1080
// 设配目标:1920 * 1080 ( 1 : 1) | 3840* 2160 ( 2 : 2 ) | 7680 * 2160 ( 4 : 2)
// 1.设计稿尺寸
let targetWidth = 1920;
let targetHeight = 1080;
let targetRatio = 16 / 9; // 宽高比率 (宽 / 高)
// 2.拿到当前设备(浏览器)的宽度
let currentWidth =
document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth;
let currentHeight =
document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight;
// 3.计算缩放比率(屏幕过宽,根据高度计算缩放比例)
let scaleRatio = currentWidth / targetWidth; // 参照宽度进行缩放(默认情况下)
// 当前宽高比例
let currentRatio = currentWidth / currentHeight;
if (currentRatio > targetRatio) {
scaleRatio = currentHeight / targetHeight; // 参照高度进行缩放(屏幕很宽的情况下)
document.body.style = `transform: scale(${scaleRatio}) translateX(-50%); left: 50%;`;
} else {
// 4.开始缩放网页
document.body.style = `transform: scale(${scaleRatio})`;
}
</script>
</html>js
xml
<script>
var lazyFun;
function init(el, width, height) {
var _el = document.getElementById(el);
var hScale = window.innerHeight / height;
var wScale = window.innerWidth / width;
_el.style.transform = 'scale(' + wScale + ',' + hScale + ')'
}
init('mainbody', 1920, 1080);
window.onresize = function() {
clearTimeout(lazyFun);
lazyFun = setTimeout(function() {
init('mainbody', 1920, 1080)
}, 100);
};
</script>四、在vue中使用
参考视频:
1. 设置缩放比例函数rem.js
xml
// 基准大小 -- 设计稿:1920 * 1080
const baseWidth = 1920;
const baseHeight = 1080;
// 设置 rem 函数
function setRem() {
// 4.开始缩放网页
document.body.style = `transform: scale(${getScale()})`;
}
// 获取缩放比例
const getScale = () => {
// 当前设备(浏览器)的宽高
let currentWidth =
document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth;
let currentHeight =
document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight;
// 计算缩放比率(屏幕过宽,根据高度计算缩放比例)
const scaleX = currentWidth / baseWidth;
const scaleY = currentHeight / baseHeight;
let scaleRatio = Math.min(scaleX, scaleY);
return scaleRatio;
}
// 计算内容距离顶部和左侧距离,使其一直处于居中状态
const getDistance = () => {
// 当前设备(浏览器)的宽高
let currentWidth =
document.documentElement.clientWidth || document.body.clientWidth;
let currentHeight =
document.documentElement.clientHeight || document.body.clientHeight;
let scaleRatio = getScale();
let left = (currentWidth - baseWidth * scaleRatio) / 2;
let top = (currentHeight - baseHeight * scaleRatio) / 2;
return { left, top }
}
// 设置 rem 函数
export default {
setRem,
getScale,
getDistance
};2. App/body全局样式
xml
<template>
<HelloWorld />
</template>
<script setup>
import HelloWorld from "./components/HelloWorld.vue";
</script>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html,
body,
#app {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
font-family: Helvetica Neue, Helvetica, PingFang SC, Hiragino Sans GB,
Microsoft YaHei, SimSun, sans-serif;
font-weight: 400;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: transparent;
background-color: #fff;
font-size: 14px;
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;
}
</style>3. 组件内使用rem.js导出的函数计算容器缩放比例和居中距离
xml
<template>
<div class="main-wapper">
<div id="main-container" class="main-container">
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import rem from "@/utils/rem";
import { onMounted } from "vue";
onMounted(() => {
init();
});
const init = () => {
// 初始化
initWindows();
// 改变窗口时重新设置rem
window.addEventListener(
"resize",
() => {
initWindows();
},
true
);
};
const initWindows = () => {
const scaleRatio = rem.getScale();
const distance = rem.getDistance();
document.getElementById(
"main-container"
).style.transform = `translate(${distance.left}px,${distance.top}px) scale(${scaleRatio})`;
};
</script>
<style>
.main-wapper {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
/* background: url("@/assets/images/bg.jpg") no-repeat center center; */
background-color: #fff;
background-size: 100% 100%;
background-size: cover;
}
.main-container {
width: 1920px;
height: 1080px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
position: fixed;
top: 0px;
left: 0px;
overflow: hidden;
transform-origin: left top;
}
ul {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr); /* 每行 3 个 li */
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
border: 3px solid rgb(38, 0, 255);
box-sizing: border-box;
gap: 10px; /* 添加 10px 的间隔 */
padding: 10px;
}
li {
font-size: 30px;
list-style: none;
border: 2px solid red;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>